
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 006
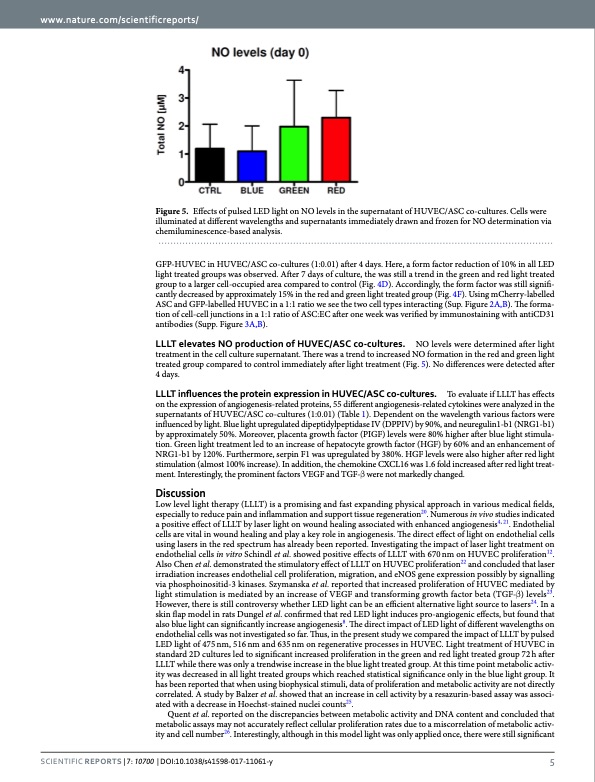
www.nature.com/scientificreports/ Figure 5. Effects of pulsed LED light on NO levels in the supernatant of HUVEC/ASC co-cultures. Cells were illuminated at different wavelengths and supernatants immediately drawn and frozen for NO determination via chemiluminescence-based analysis. GFP-HUVEC in HUVEC/ASC co-cultures (1:0.01) after 4 days. Here, a form factor reduction of 10% in all LED light treated groups was observed. After 7 days of culture, the was still a trend in the green and red light treated group to a larger cell-occupied area compared to control (Fig. 4D). Accordingly, the form factor was still signifi- cantly decreased by approximately 15% in the red and green light treated group (Fig. 4F). Using mCherry-labelled ASC and GFP-labelled HUVEC in a 1:1 ratio we see the two cell types interacting (Sup. Figure 2A,B). The forma- tion of cell-cell junctions in a 1:1 ratio of ASC:EC after one week was verified by immunostaining with antiCD31 antibodies (Supp. Figure 3A,B). LLLT elevates NO production of HUVEC/ASC co-cultures. NO levels were determined after light treatment in the cell culture supernatant. There was a trend to increased NO formation in the red and green light treated group compared to control immediately after light treatment (Fig. 5). No differences were detected after 4 days. LLLT influences the protein expression in HUVEC/ASC co-cultures. To evaluate if LLLT has effects on the expression of angiogenesis-related proteins, 55 different angiogenesis-related cytokines were analyzed in the supernatants of HUVEC/ASC co-cultures (1:0.01) (Table 1). Dependent on the wavelength various factors were influenced by light. Blue light upregulated dipeptidylpeptidase IV (DPPIV) by 90%, and neuregulin1-b1 (NRG1-b1) by approximately 50%. Moreover, placenta growth factor (PIGF) levels were 80% higher after blue light stimula- tion. Green light treatment led to an increase of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) by 60% and an enhancement of NRG1-b1 by 120%. Furthermore, serpin F1 was upregulated by 380%. HGF levels were also higher after red light stimulation (almost 100% increase). In addition, the chemokine CXCL16 was 1.6 fold increased after red light treat- ment. Interestingly, the prominent factors VEGF and TGF-β were not markedly changed. Discussion Low level light therapy (LLLT) is a promising and fast expanding physical approach in various medical fields, especially to reduce pain and inflammation and support tissue regeneration20. Numerous in vivo studies indicated a positive effect of LLLT by laser light on wound healing associated with enhanced angiogenesis4, 21. Endothelial cells are vital in wound healing and play a key role in angiogenesis. The direct effect of light on endothelial cells using lasers in the red spectrum has already been reported. Investigating the impact of laser light treatment on endothelial cells in vitro Schindl et al. showed positive effects of LLLT with 670 nm on HUVEC proliferation12. Also Chen et al. demonstrated the stimulatory effect of LLLT on HUVEC proliferation22 and concluded that laser irradiation increases endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and eNOS gene expression possibly by signalling via phosphoinositid-3 kinases. Szymanska et al. reported that increased proliferation of HUVEC mediated by light stimulation is mediated by an increase of VEGF and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) levels23. However, there is still controversy whether LED light can be an efficient alternative light source to lasers24. In a skin flap model in rats Dungel et al. confirmed that red LED light induces pro-angiogenic effects, but found that also blue light can significantly increase angiogenesis8. The direct impact of LED light of different wavelengths on endothelial cells was not investigated so far. Thus, in the present study we compared the impact of LLLT by pulsed LED light of 475 nm, 516 nm and 635 nm on regenerative processes in HUVEC. Light treatment of HUVEC in standard 2D cultures led to significant increased proliferation in the green and red light treated group 72 h after LLLT while there was only a trendwise increase in the blue light treated group. At this time point metabolic activ- ity was decreased in all light treated groups which reached statistical significance only in the blue light group. It has been reported that when using biophysical stimuli, data of proliferation and metabolic activity are not directly correlated. A study by Balzer et al. showed that an increase in cell activity by a resazurin-based assay was associ- ated with a decrease in Hoechst-stained nuclei counts25. Quent et al. reported on the discrepancies between metabolic activity and DNA content and concluded that metabolic assays may not accurately reflect cellular proliferation rates due to a miscorrelation of metabolic activ- ity and cell number26. Interestingly, although in this model light was only applied once, there were still significant SCientifiC REpORTS | 7: 10700 | DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-11061-y 5PDF Image | impact of wavelengths of LED light-therapy on endothelial cells
PDF Search Title:
impact of wavelengths of LED light-therapy on endothelial cellsOriginal File Name Searched:
Rohringeretal-LLLT2017.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Cruise Ship Reviews | Luxury Resort | Jet | Yacht | and Travel Tech More Info
Cruising Review Topics and Articles More Info
Software based on Filemaker for the travel industry More Info
The Burgenstock Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
Resort Reviews: World Class resorts... More Info
The Riffelalp Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@cruisingreview.com | RSS | AMP |