
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 004
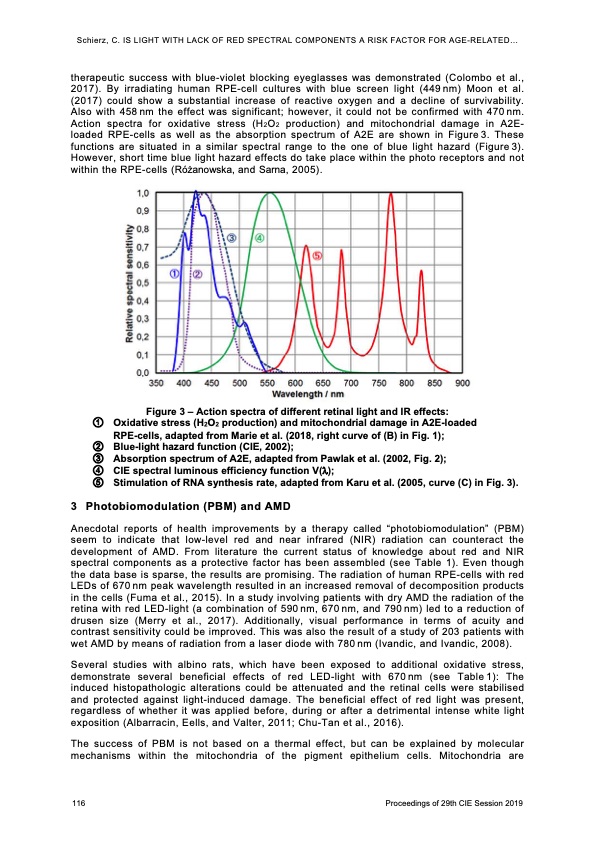
Schierz, C. IS LIGHT WITH LACK OF RED SPECTRAL COMPONENTS A RISK FACTOR FOR AGE-RELATED... therapeutic success with blue-violet blocking eyeglasses was demonstrated (Colombo et al., 2017). By irradiating human RPE-cell cultures with blue screen light (449nm) Moon et al. (2017) could show a substantial increase of reactive oxygen and a decline of survivability. Also with 458nm the effect was significant; however, it could not be confirmed with 470nm. Action spectra for oxidative stress (H2O2 production) and mitochondrial damage in A2E- loaded RPE-cells as well as the absorption spectrum of A2E are shown in Figure3. These functions are situated in a similar spectral range to the one of blue light hazard (Figure3). However, short time blue light hazard effects do take place within the photo receptors and not within the RPE-cells (Różanowska, and Sarna, 2005). Figure 3 – Action spectra of different retinal light and IR effects: 1 Oxidative stress (H2O2 production) and mitochondrial damage in A2E-loaded RPE-cells, adapted from Marie et al. (2018, right curve of (B) in Fig. 1); 2 Blue-light hazard function (CIE, 2002); 3 Absorption spectrum of A2E, adapted from Pawlak et al. (2002, Fig. 2); 4 CIE spectral luminous efficiency function V(); 5 Stimulation of RNA synthesis rate, adapted from Karu et al. (2005, curve (C) in Fig. 3). 3 Photobiomodulation (PBM) and AMD Anecdotal reports of health improvements by a therapy called “photobiomodulation” (PBM) seem to indicate that low-level red and near infrared (NIR) radiation can counteract the development of AMD. From literature the current status of knowledge about red and NIR spectral components as a protective factor has been assembled (see Table 1). Even though the data base is sparse, the results are promising. The radiation of human RPE-cells with red LEDs of 670 nm peak wavelength resulted in an increased removal of decomposition products in the cells (Fuma et al., 2015). In a study involving patients with dry AMD the radiation of the retina with red LED-light (a combination of 590 nm, 670 nm, and 790 nm) led to a reduction of drusen size (Merry et al., 2017). Additionally, visual performance in terms of acuity and contrast sensitivity could be improved. This was also the result of a study of 203 patients with wet AMD by means of radiation from a laser diode with 780 nm (Ivandic, and Ivandic, 2008). Several studies with albino rats, which have been exposed to additional oxidative stress, demonstrate several beneficial effects of red LED-light with 670nm (see Table1): The induced histopathologic alterations could be attenuated and the retinal cells were stabilised and protected against light-induced damage. The beneficial effect of red light was present, regardless of whether it was applied before, during or after a detrimental intense white light exposition (Albarracin, Eells, and Valter, 2011; Chu-Tan et al., 2016). The success of PBM is not based on a thermal effect, but can be explained by molecular mechanisms within the mitochondria of the pigment epithelium cells. Mitochondria are 116 Proceedings of 29th CIE Session 2019PDF Image | LIGHT WITH LACK OF RED SPECTRAL COMPONENTS v amd
PDF Search Title:
LIGHT WITH LACK OF RED SPECTRAL COMPONENTS v amdOriginal File Name Searched:
x046-OP20.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Cruise Ship Reviews | Luxury Resort | Jet | Yacht | and Travel Tech More Info
Cruising Review Topics and Articles More Info
Software based on Filemaker for the travel industry More Info
The Burgenstock Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
Resort Reviews: World Class resorts... More Info
The Riffelalp Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@cruisingreview.com | RSS | AMP |