
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 007
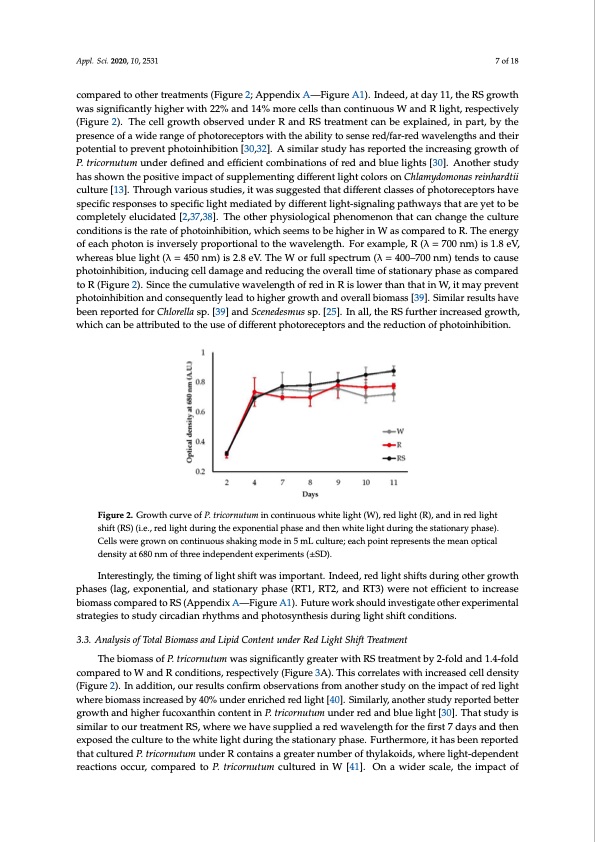
Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, x FOR PEER REVIEW 7 of 22 in the same study, they have reported that the supplementation of blue light to yellow light is better for stable cultivation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2531 The growth of microalgae in mixotrophic conditions is an interesting choice for enhancing the productivity of particular metabolites, which will vary according to the product of interest wanted [31]. However, there are cost-effective and economic advantages to growth in mixotrophy if the compared tocoartbhoenrsoturercaetims denritvsed(Ffriogmucrheea2p; AwapstpeerensdouixrceAs s—ucFhiagsuagrericAul1tu)r.alInandemedun,iacitpadlawyas1te1w,atthere RS growth that are rich in micronutrients and carbon sources [32]. There has been in-depth research conducted was significantly higher with 22% and 14% more cells than continuous W and R light, respectively on the impact of varied carbon source such as glucose, fructose, and glycerol on enhancing the (Figure 2). The cell growth observed under R and RS treatment can be explained, in part, by the biomass of P. tricornutum [31,33]. A relevant point to consider when comparing results from red light presence of awwithidtheorseanofgredolifgphthcomtobriencedepwtiothrbsluwe,itohr otther awbaivleilteyngttohsiesnthsaet trheedm/foanro-crherdomwataicvreldelnigghths and their corresponds to the absence of the others. However, our results, combined with findings from several potential to prevent photoinhibition [30,32]. A similar study has reported the increasing growth of published studies, have shown the importance of monochromatic light or the mixing of wavelengths P. tricornutum under defined and efficient combinations of red and blue lights [30]. Another study on the biomass and lipid production in different microalgae species as discussed above [7,13,25,26]. has shown thTehispmoostiitviavtediumsptoafcutrtohefrsouptpimpilzemthenpthiontogaudtoifftroeprehinctcolnigdhititoncso.lors on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii culture [13]. Through various studies, it was suggested that different classes of photoreceptors have 3.2. Growth Curve Analysis of P. tricornutum during Red Light Shift specific responses to specific light mediated by different light-signaling pathways that are yet to be Studies have reported that light color and intensity bring changes in the photon flux density, completely elucidated [2,37,38]. The other physiological phenomenon that can change the culture which have a strong impact on growth and metabolic pathways [32,33]. Photoautotrophic conditions conditionsisctrheaetercaetretaoinflipmhitoatioinnshwihbeintigornow,nwinhibciohresaecetomrssbetcoaubsesheilfg-sheardiingbWymaiscrcooalmgaplcaerllesdinthoigRh-.Theenergy density cultures limits the light available for growth, which can be confirmed in lab-scale experiments of each photon is inversely proportional to the wavelength. For example, R (λ = 700 nm) is 1.8 eV, by observing the growth curve. Therefore, to reduce the impact of either loss of light as heat or self- whereas blue light (λ = 450 nm) is 2.8 eV. The W or full spectrum (λ = 400–700 nm) tends to cause shading, the strategy of light shifting from one spectrum to another can trigger different photoinhibitipohno,toirnecdeuptcoirnsgtocaecltlivdataemdiaffgereenatnlidghrte-sdiguncailingpthatehwoavyesr,alllowtiimngeaobfesttteartcionvaersyiopnhofalsigehatscompared energy [34–36]. Therefore, we investigated the effect of red light shifts on P. tricornutum growth to R (Figure 2). Since the cumulative wavelength of red in R is lower than that in W, it may prevent during different growth phases under batch cultivation for 11 days. photoinhibition and consequently lead to higher growth and overall biomass [39]. Similar results have P. tricornutum grown in red light until the end of exponential phase (from day 1 to 7) and then been reportesdhiftoedr tCohwlhoirtelligahstp(R.S[)3s9ho]waenddthSecgerneaetdesetsgmrouwsthspco.m[p2a5r]e.dItno aalllol,thtehrecoRndSitfiounrstthesetredin(Fcigrueraesed growth, 2, Appendix A—Figure A1). In addition, RS is significantly better to promote growth compared to which can be attributed to the use of different photoreceptors and the reduction of photoinhibition. continuous white (W) or red light (R) (Figure 2). 7 of 18 Figure 2. Growth curve of P. tricornutum in continuous white light (W), red light (R), and in red light Figure 2. Growth curve of P. tricornutum in continuous white light (W), red light (R), and in red light shift (RS) (i.e., red light during the exponential phase and then white light during the stationary shift (RS) (i.e., red light during the exponential phase and then white light during the stationary phase). phase). Cells were grown on continuous shaking mode in 5 mL culture; each point represents the Cells were grown on continuous shaking mode in 5 mL culture; each point represents the mean optical mean optical density at 680 nm of three independent experiments (±SD). density at 680 nm of three independent experiments (±SD). P. tricornutum cultured cells were adapting to each condition in a similar manner during the 3.3. Analysis of Total Biomass and Lipid Content under Red Light Shift Treatment The biomass of P. tricornutum was significantly greater with RS treatment by 2-fold and 1.4-fold compared to W and R conditions, respectively (Figure 3A). This correlates with increased cell density (Figure 2). In addition, our results confirm observations from another study on the impact of red light where biomass increased by 40% under enriched red light [40]. Similarly, another study reported better growth and higher fucoxanthin content in P. tricornutum under red and blue light [30]. That study is similar to our treatment RS, where we have supplied a red wavelength for the first 7 days and then exposed the culture to the white light during the stationary phase. Furthermore, it has been reported that cultured P. tricornutum under R contains a greater number of thylakoids, where light-dependent reactions occur, compared to P. tricornutum cultured in W [41]. On a wider scale, the impact of adaptation and exponential phases (Figure 2). It should be noted that there seems to be a crucial lag Interestingly, the timing of light shift was important. Indeed, red light shifts during other growth phases (lag, exponential, and stationary phase (RT1, RT2, and RT3) were not efficient to increase biomass compared to RS (Appendix A—Figure A1). Future work should investigate other experimental strategies to study circadian rhythms and photosynthesis during light shift conditions.PDF Image | Red Light Variation Lipid Profiles in Phaeodactylum tricornutum
PDF Search Title:
Red Light Variation Lipid Profiles in Phaeodactylum tricornutumOriginal File Name Searched:
applsci-10-02531.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Cruise Ship Reviews | Luxury Resort | Jet | Yacht | and Travel Tech More Info
Cruising Review Topics and Articles More Info
Software based on Filemaker for the travel industry More Info
The Burgenstock Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
Resort Reviews: World Class resorts... More Info
The Riffelalp Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@cruisingreview.com | RSS | AMP |