
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 012
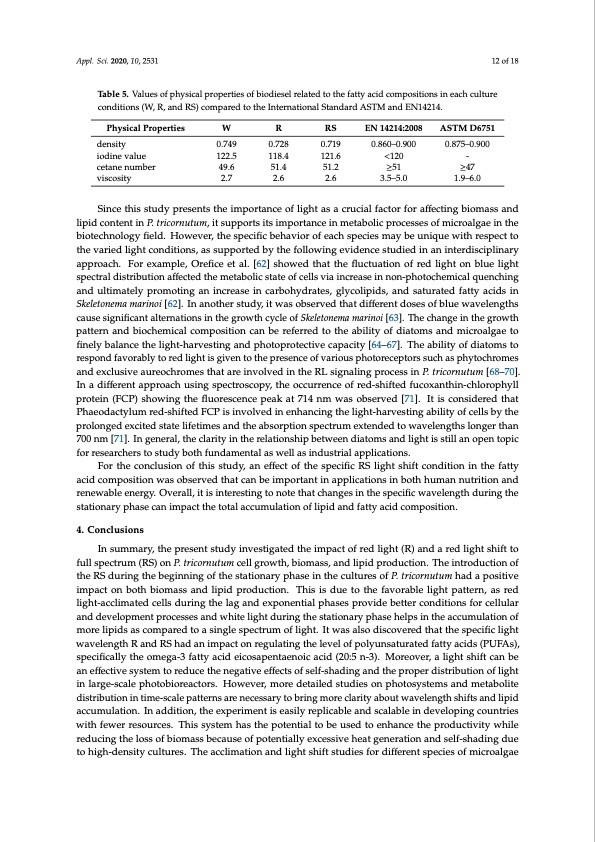
Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2531 12 of 18 Table 5. Values of physical properties of biodiesel related to the fatty acid compositions in each culture conditions (W, R, and RS) compared to the International Standard ASTM and EN14214. Physical Properties density iodine value cetane number viscosity W R 0.749 0.728 122.5 118.4 49.6 51.4 2.7 2.6 RS EN 14214:2008 0.719 0.860–0.900 121.6 <120 51.2 ≥51 2.6 3.5–5.0 ASTM D6751 0.875–0.900 - ≥47 1.9–6.0 Since this study presents the importance of light as a crucial factor for affecting biomass and lipid content in P. tricornutum, it supports its importance in metabolic processes of microalgae in the biotechnology field. However, the specific behavior of each species may be unique with respect to the varied light conditions, as supported by the following evidence studied in an interdisciplinary approach. For example, Orefice et al. [62] showed that the fluctuation of red light on blue light spectral distribution affected the metabolic state of cells via increase in non-photochemical quenching and ultimately promoting an increase in carbohydrates, glycolipids, and saturated fatty acids in Skeletonema marinoi [62]. In another study, it was observed that different doses of blue wavelengths cause significant alternations in the growth cycle of Skeletonema marinoi [63]. The change in the growth pattern and biochemical composition can be referred to the ability of diatoms and microalgae to finely balance the light-harvesting and photoprotective capacity [64–67]. The ability of diatoms to respond favorably to red light is given to the presence of various photoreceptors such as phytochromes and exclusive aureochromes that are involved in the RL signaling process in P. tricornutum [68–70]. In a different approach using spectroscopy, the occurrence of red-shifted fucoxanthin-chlorophyll protein (FCP) showing the fluorescence peak at 714 nm was observed [71]. It is considered that Phaeodactylum red-shifted FCP is involved in enhancing the light-harvesting ability of cells by the prolonged excited state lifetimes and the absorption spectrum extended to wavelengths longer than 700 nm [71]. In general, the clarity in the relationship between diatoms and light is still an open topic for researchers to study both fundamental as well as industrial applications. For the conclusion of this study, an effect of the specific RS light shift condition in the fatty acid composition was observed that can be important in applications in both human nutrition and renewable energy. Overall, it is interesting to note that changes in the specific wavelength during the stationary phase can impact the total accumulation of lipid and fatty acid composition. 4. Conclusions In summary, the present study investigated the impact of red light (R) and a red light shift to full spectrum (RS) on P. tricornutum cell growth, biomass, and lipid production. The introduction of the RS during the beginning of the stationary phase in the cultures of P. tricornutum had a positive impact on both biomass and lipid production. This is due to the favorable light pattern, as red light-acclimated cells during the lag and exponential phases provide better conditions for cellular and development processes and white light during the stationary phase helps in the accumulation of more lipids as compared to a single spectrum of light. It was also discovered that the specific light wavelength R and RS had an impact on regulating the level of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), specifically the omega-3 fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5 n-3). Moreover, a light shift can be an effective system to reduce the negative effects of self-shading and the proper distribution of light in large-scale photobioreactors. However, more detailed studies on photosystems and metabolite distribution in time-scale patterns are necessary to bring more clarity about wavelength shifts and lipid accumulation. In addition, the experiment is easily replicable and scalable in developing countries with fewer resources. This system has the potential to be used to enhance the productivity while reducing the loss of biomass because of potentially excessive heat generation and self-shading due to high-density cultures. The acclimation and light shift studies for different species of microalgaePDF Image | Red Light Variation Lipid Profiles in Phaeodactylum tricornutum
PDF Search Title:
Red Light Variation Lipid Profiles in Phaeodactylum tricornutumOriginal File Name Searched:
applsci-10-02531.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Cruise Ship Reviews | Luxury Resort | Jet | Yacht | and Travel Tech More Info
Cruising Review Topics and Articles More Info
Software based on Filemaker for the travel industry More Info
The Burgenstock Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
Resort Reviews: World Class resorts... More Info
The Riffelalp Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@cruisingreview.com | RSS | AMP |