
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 004
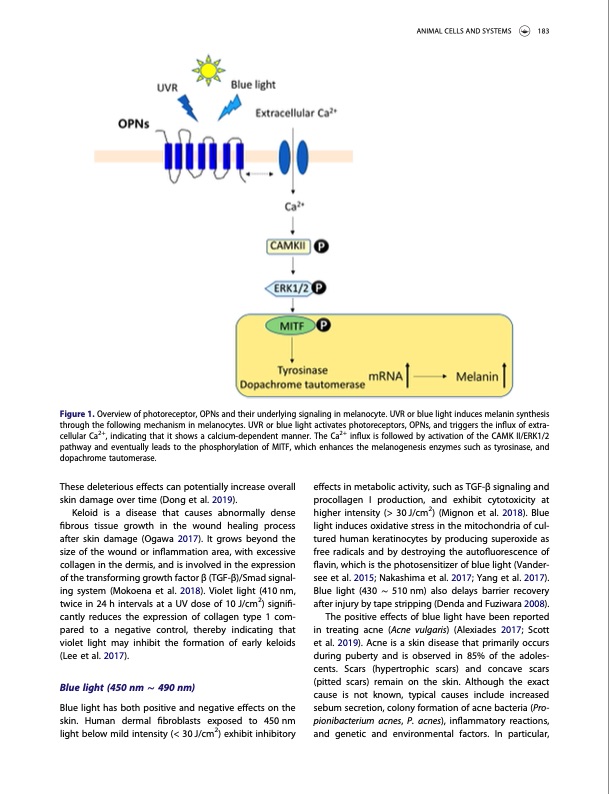
Figure 1. Overview of photoreceptor, OPNs and their underlying signaling in melanocyte. UVR or blue light induces melanin synthesis through the following mechanism in melanocytes. UVR or blue light activates photoreceptors, OPNs, and triggers the influx of extra- cellular Ca2+, indicating that it shows a calcium-dependent manner. The Ca2+ influx is followed by activation of the CAMK II/ERK1/2 pathway and eventually leads to the phosphorylation of MITF, which enhances the melanogenesis enzymes such as tyrosinase, and dopachrome tautomerase. These deleterious effects can potentially increase overall skin damage over time (Dong et al. 2019). Keloid is a disease that causes abnormally dense fibrous tissue growth in the wound healing process after skin damage (Ogawa 2017). It grows beyond the size of the wound or inflammation area, with excessive collagen in the dermis, and is involved in the expression of the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)/Smad signal- ing system (Mokoena et al. 2018). Violet light (410 nm, twice in 24 h intervals at a UV dose of 10 J/cm2) signifi- cantly reduces the expression of collagen type 1 com- pared to a negative control, thereby indicating that violet light may inhibit the formation of early keloids (Lee et al. 2017). Blue light (450 nm ∼ 490 nm) Blue light has both positive and negative effects on the skin. Human dermal fibroblasts exposed to 450nm light below mild intensity (< 30 J/cm2) exhibit inhibitory effects in metabolic activity, such as TGF-β signaling and procollagen I production, and exhibit cytotoxicity at higher intensity (> 30 J/cm2) (Mignon et al. 2018). Blue light induces oxidative stress in the mitochondria of cul- tured human keratinocytes by producing superoxide as free radicals and by destroying the autofluorescence of flavin, which is the photosensitizer of blue light (Vander- see et al. 2015; Nakashima et al. 2017; Yang et al. 2017). Blue light (430 ∼ 510 nm) also delays barrier recovery after injury by tape stripping (Denda and Fuziwara 2008). The positive effects of blue light have been reported in treating acne (Acne vulgaris) (Alexiades 2017; Scott et al. 2019). Acne is a skin disease that primarily occurs during puberty and is observed in 85% of the adoles- cents. Scars (hypertrophic scars) and concave scars (pitted scars) remain on the skin. Although the exact cause is not known, typical causes include increased sebum secretion, colony formation of acne bacteria (Pro- pionibacterium acnes, P. acnes), inflammatory reactions, and genetic and environmental factors. In particular, ANIMAL CELLS AND SYSTEMS 183PDF Image | Various biological effects of solar radiation on skin
PDF Search Title:
Various biological effects of solar radiation on skinOriginal File Name Searched:
biological-effects-solar-radiation-phototherapy.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Cruise Ship Reviews | Luxury Resort | Jet | Yacht | and Travel Tech More Info
Cruising Review Topics and Articles More Info
Software based on Filemaker for the travel industry More Info
The Burgenstock Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
Resort Reviews: World Class resorts... More Info
The Riffelalp Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@cruisingreview.com | RSS | AMP |