
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 005
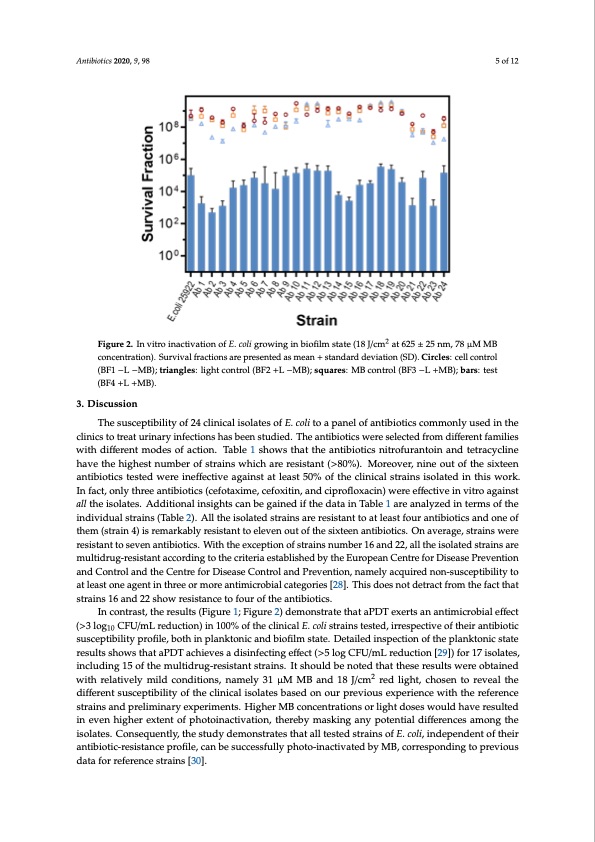
Antibiotics 2019, 8, x 1 of 12 Antibiotics 2020, 9, 98 5 of 12 Figure 2. In vitro inactivation of E. coli growing in biofilm state (18 J/cm2 at 625 ± 25 nm, 78 μM MB concentration). Survival fractions are presented as mean + standard deviation (SD). Circles: cell control Figure 2. In vitro inactivation of E. coli growing in biofilm state (18 J/cm2 at 625 ± 25 nm, 78 μ M MB (BF1 −L −MB); triangles: light control (BF2 +L −MB); squares: MB control (BF3 −L +MB); bars: test concentration). Survival fractions are presented as mean + standard deviation (SD). Circles: cell (BF4 +L +MB). control (BF1 −L −MB); triangles: light control (BF2 +L −MB); squares: MB control (BF3 −L +MB); bars: test (BF4 +L +MB). 3. Discussion Control experiments showed that the effect of light or MB alone is negligible for all strains (p > The susceptibility of 24 clinical isolates of E. coli to a panel of antibiotics commonly used in the 0.9). On the other hand, there were significant differences among the control and the PDT-treated clinics to treat urinary infections has been studied. The antibiotics were selected from different families groups (p < 0.0001) and there were also significant differences in PDT susceptibility among the strains with different modes of action. Table 1 shows that the antibiotics nitrofurantoin and tetracycline (p = 0.0007). have the highest number of strains which are resistant (>80%). Moreover, nine out of the sixteen antibiotics tested were ineffective against at least 50% of the clinical strains isolated in this work. 3. Discussion In fact, only three antibiotics (cefotaxime, cefoxitin, and ciprofloxacin) were effective in vitro against The susceptibility of 24 clinical isolates of E. coli to a panel of antibiotics commonly used in the all the isolates. Additional insights can be gained if the data in Table 1 are analyzed in terms of the clinics to treat urinary infections has been studied. The antibiotics were selected from different individual strains (Table 2). All the isolated strains are resistant to at least four antibiotics and one of families with different modes of action. Table 1 shows that the antibiotics nitrofurantoin and them (strain 4) is remarkably resistant to eleven out of the sixteen antibiotics. On average, strains were tetracycline have the highest number of strains which are resistant (>80%). Moreover, nine out of the resistant to seven antibiotics. With the exception of strains number 16 and 22, all the isolated strains are sixteen antibiotics tested were ineffective against at least 50% of the clinical strains isolated in this multidrug-resistant according to the criteria established by the European Centre for Disease Prevention work. In fact, only three antibiotics (cefotaxime, cefoxitin, and ciprofloxacin) were effective in vitro and Control and the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, namely acquired non-susceptibility to against all the isolates. Additional insights can be gained if the data in Table 1 are analyzed in terms at least one agent in three or more antimicrobial categories [28]. This does not detract from the fact that of the individual strains (Table 2). All the isolated strains are resistant to at least four antibiotics and strains 16 and 22 show resistance to four of the antibiotics. one of them (strain 4) is remarkably resistant to eleven out of the sixteen antibiotics. On average, In contrast, the results (Figure 1; Figure 2) demonstrate that aPDT exerts an antimicrobial effect strains were resistant to seven antibiotics. With the exception of strains number 16 and 22, all the (>3 log10 CFU/mL reduction) in 100% of the clinical E. coli strains tested, irrespective of their antibiotic isolated strains are multidrug-resistant according to the criteria established by the European Centre susceptibility profile, both in planktonic and biofilm state. Detailed inspection of the planktonic state for Disease Prevention and Control and the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, namely results shows that aPDT achieves a disinfecting effect (>5 log CFU/mL reduction [29]) for 17 isolates, acquired non-susceptibility to at least one agent in three or more antimicrobial categories [28]. This including 15 of the multidrug-resistant strains. It should be noted that these results were obtained does not detract from the fact that strains 16 and 22 show resistance to four of the antibiotics. with relatively mild conditions, namely 31 μM MB and 18 J/cm2 red light, chosen to reveal the different susceptibility of the clinical isolates based on our previous experience with the reference strains and preliminary experiments. Higher MB concentrations or light doses would have resulted in even higher extent of photoinactivation, thereby masking any potential differences among the isolates. Consequently, the study demonstrates that all tested strains of E. coli, independent of their antibiotic-resistance profile, can be successfully photo-inactivated by MB, corresponding to previous data for reference strains [30].PDF Image | Effective Photodynamic Inactivation of 26 E coli Strains
PDF Search Title:
Effective Photodynamic Inactivation of 26 E coli StrainsOriginal File Name Searched:
antibiotics-09-00098-v2.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Cruise Ship Reviews | Luxury Resort | Jet | Yacht | and Travel Tech More Info
Cruising Review Topics and Articles More Info
Software based on Filemaker for the travel industry More Info
The Burgenstock Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
Resort Reviews: World Class resorts... More Info
The Riffelalp Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@cruisingreview.com | RSS | AMP |