
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 014
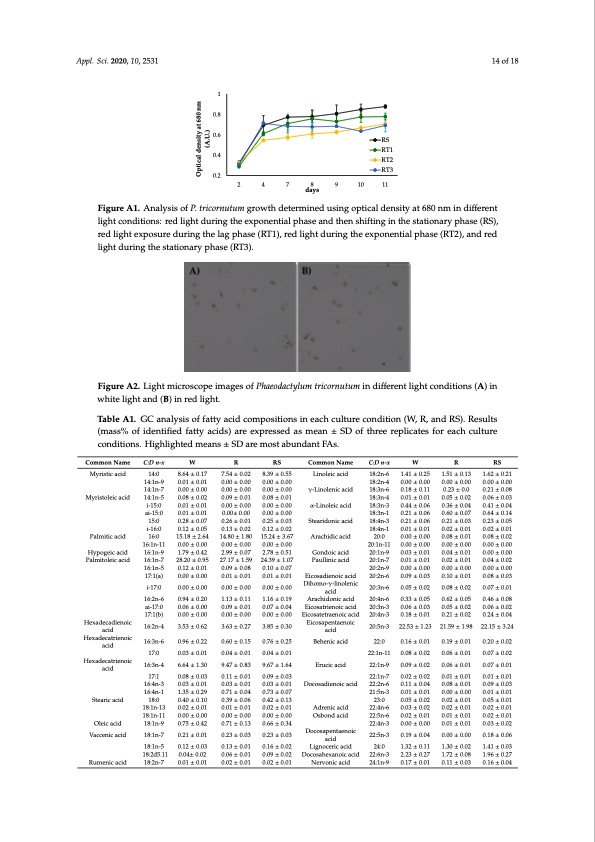
bring changes in the photon flux density, which have a strong impact on the growth and metabolic Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2531 pathways [31,56]. Light shift from one spectrum to another will change the light ambience and culture environment, which can trigger different photoreceptors to activate signaling pathways allowing a better conversion of light energy. However, the exact growth phase on which to exert a light shift is unknown. Thus, we investigated the effect of red light shift on P. tricornutum growth during different growth phases under batch cultivation for 10 days (Appendix A—Figure A1). Specifically, the effect on growth was studied using optical density for six conditions. The impact of red light shift to a full spectrum during different growth phases i.e., lag, exponential, and stationary are labeled as RT1, RT2, RT3; RS (Table 2), along with continuous red light (R), was investigated. RT2 and RT3 were found to be less effective at promoting growth, whereas RS was significantly better to promote P. tricornutum growth (Appendix A—Figure A1). Appl. S 16 of 22 and to d day 7 (expogdown (Figure A1). However, RT1, RT2, and RT3 could be interesting parameters to consider for studying Figure A1. Analysis of P. tricornutum growth determined using optical density at 680 nm in different 14 of 18 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 ci. 2020, 10, x FOR PEER REVIEW 0.2 RS RT1 RT2 RT3 2 4 7 8 9 10 11 tal lipid count. Similarly as observed in Figure 2, a lag is observed between day 4 an nential to stationary) where it is not clear whether cell growth continued before slowin days Figure A1. AnalysisbonaflfiigPdhe.t mctoerntdiaicbtiolnriscn: rpueadthliuwghmatydsugrininrgdotihawetoemtxhpsonodennceteiattlehperhrameseisainmdeothrdeninsuhfoisfrtimngatgiinotnhoeopsntattihiocenacrhlyapdrahecatsener(isRzSai)t,iyon aoft 680 nm in different these photoreceptors such as phytochromes. red light exposure during the lag phase (RT1), red light during the exponential phase (RT2), and red lightconditions:redligCheltlmdourprhionlogytihsseomeextimpeosninedincativaelopfchaansgesiannredspotnhsetnosstrhesisf.tTihnregeminorpthhoteypsestationaryphase(RS), light during the stationary phase (RT3). in P. tricornutum culture have been reported: oval, fusiform and triradiate [48]. Microscopic analyses red light exposure during the lag phase (RT1), red light during the exponential phase (RT2), and red (FigTuhre4rce,d)lirgehvtesahleifdt tarehaigtmheonctcudrurreincgetohfefsupseifcoifrimc gcreolwls,tha lpimhaisteds—nulamg,bexrpoofntreinratidaila, aten-dshsatapteidoncaerlyls, pahnadsen(oRaTp1p, eRaTr2a,nacnedofRtTh3e)—ovwalafsonrmot iannaelflfoicfioenutr mgreotwhothd ctonindcitrieoansse. gHrowtehve(Fr,igouresAtu1d)y. Tshuosw, ethdetshee light during the stationary phase (RT3). trperaetsmenecnetsoafraelnimotitiendtenruesmtibnegr fofrtroiurardiniavtescteigllasti(oAnp,pseincdeixw—eFaiigmueredAto2)e.nhance the overall biomass Figure A2. Light microscope images of Phaeodactylum tricornutum in different light conditions (A) in Figure A2. Light microscope images of Phaeodactylum tricornutum in different light conditions (A) in white light and (B) in red light. white light and (B) in red light. Table A1. GC analysis of fatty acid compositions in each culture condition (W, R, and RS). Results (mass% of identified fatty acids) are expressed as mean ± SD of three replicates for each culture conditions. Highlighted means ± SD are most abundant FAs. Common Name Myristic acid Myristoleic acid Palmitic acid Hypogeic acid Palmitoleic acid Hexadecadienoic acid Hexadecatrienoic acid Hexadecatrienoic acid Stearic acid Oleic acid Vaccenic acid Rumenic acid C:D n-x 14:0 14:1n-9 14:1n-7 14:1n-5 i-15:0 ai-15:0 15:0 i-16:0 16:0 16:1n-11 16:1n-9 16:1n-7 16:1n-5 17:1(a) i-17:0 16:2n-6 ai-17:0 17:1(b) 16:2n-4 16:3n-6 17:0 16:3n-4 17:1 16:4n-3 16:4n-1 18:0 18:1n-13 18:1n-11 18:1n-9 18:1n-7 18:1n-5 18:2d5.11 18:2n-7 W 8.64 ± 0.17 0.01 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.08 ± 0.02 0.01 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.01 0.28 ± 0.07 0.12 ± 0.05 15.18 ± 2.64 0.00 ± 0.00 1.79 ± 0.42 28.20 ± 0.95 0.12 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.00 ± 0.00 0.94 ± 0.20 0.06 ± 0.00 0.00 ± 0.00 3.53 ± 0.62 0.96 ± 0.22 0.03 ± 0.01 6.64 ± 1.30 0.08 ± 0.03 0.03 ± 0.01 1.35 ± 0.29 0.40 ± 0.10 0.02 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.75 ± 0.42 0.21 ± 0.01 0.12 ± 0.03 0.04± 0.02 0.01 ± 0.01 R RS 8.39 ± 0.55 0.00 ± 0.00 0.00 ± 0.00 0.08 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.00 ± 0.00 0.25 ± 0.03 0.12 ± 0.02 15.24 ± 3.67 0.00 ± 0.00 2.78 ± 0.51 24.39 ± 1.07 0.10 ± 0.07 0.01 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 1.16 ± 0.19 0.07 ± 0.04 0.00 ± 0.00 3.85 ± 0.30 0.76 ± 0.25 0.04 ± 0.01 9.67 ± 1.64 0.09 ± 0.03 0.03 ± 0.01 0.73 ± 0.07 0.42 ± 0.13 0.02 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.66 ± 0.34 0.23 ± 0.03 0.16 ± 0.02 0.09 ± 0.02 0.02 ± 0.01 Common Name Linoleic acid γ-Linolenic acid α-Linoleic acid Stearidonic acid Arachidic acid Gondoic acid Paullinic acid C:D n-x 18:2n-6 18:2n-4 18:3n-6 18:3n-4 18:3n-3 18:3n-1 18:4n-3 18:4n-1 20:0 20:1n-11 20:1n-9 20:1n-7 20:2n-9 20:2n-6 W 1.41 ± 0.25 0.00 ± 0.00 0.18 ± 0.11 0.01 ± 0.01 0.44 ± 0.06 0.21 ± 0.06 0.21 ± 0.06 0.01 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.00 ± 0.00 0.03 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.09 ± 0.03 0.05 ± 0.02 0.33 ± 0.05 0.06 ± 0.03 0.18 ± 0.01 22.53 ± 1.23 0.16 ± 0.01 0.08 ± 0.02 0.09 ± 0.02 0.02 ± 0.02 0.11 ± 0.04 0.01 ± 0.01 0.05 ± 0.02 0.03 ± 0.02 0.02 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.19 ± 0.04 1.32 ± 0.11 2.23 ± 0.27 0.17 ± 0.01 R 1.51 ± 0.13 0.00 ± 0.00 0.23 ± 0.0 0.05 ± 0.02 0.36 ± 0.04 0.60 ± 0.07 0.21 ± 0.03 0.02 ± 0.01 0.08 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.04 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.10 ± 0.01 0.08 ± 0.02 0.62 ± 0.05 0.05 ± 0.02 0.21 ± 0.02 21.59 ± 1.98 0.19 ± 0.01 0.06 ± 0.01 0.06 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.01 0.08 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.02 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 1.30 ± 0.02 1.72 ± 0.08 0.11 ± 0.03 RS 1.62 ± 0.21 0.00 ± 0.00 0.21 ± 0.08 0.06 ± 0.03 0.41 ± 0.04 0.64 ± 0.14 0.23 ± 0.05 0.02 ± 0.01 0.08 ± 0.02 0.00 ± 0.00 0.00 ± 0.00 0.04 ± 0.02 0.00 ± 0.00 0.08 ± 0.03 0.07 ± 0.01 0.46 ± 0.08 0.06 ± 0.02 0.24 ± 0.04 22.15 ± 3.24 0.20 ± 0.02 0.07 ± 0.02 0.07 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.01 0.09 ± 0.03 0.01 ± 0.01 0.05 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 0.03 ± 0.02 0.18 ± 0.06 1.41 ± 0.03 1.96 ± 0.27 0.16 ± 0.04 7.54 ± 0.00 ± 0.00 ± 0.09 ± 0.00 ± 0.00± 0.00 0.26 ± 0.01 0.13 ± 0.02 14.80 ± 1.80 0.00 ± 0.00 2.99 ± 0.07 27.17 ± 1.59 0.09 ± 0.08 0.01 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 1.13 ± 0.11 0.09 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 3.63 ± 0.27 0.60 ± 0.15 0.04 ± 0.01 9.47 ± 0.83 0.11 ± 0.01 0.03 ± 0.01 0.71 ± 0.04 0.39 ± 0.06 0.01 ± 0.01 0.00 ± 0.00 0.71 ± 0.13 0.23 ± 0.03 0.13 ± 0.01 0.06 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 Eicosadienoic acid Dihomo-γ-linolenic 20:3n-6 acid Arachidonic acid Eicosatrienoic acid Eicosatetraenoic acid Eicosapentaenoic acid Behenic acid Erucic acid Docosadienoic acid Adrenic acid Osbond acid 20:4n-6 20:3n-3 20:4n-3 20:5n-3 22:0 22:1n-11 22:1n-9 22:1n-7 22:2n-6 21:5n-3 23:0 22:4n-6 22:5n-6 22:4n-3 Docosapentaenoic 22:5n-3 acid Lignoceric acid Docosahexanoic acid Nervonic acid 24:0 22:6n-3 24:1n-9 Optical density at 680 nm (A.U.)PDF Image | Red Light Variation Lipid Profiles in Phaeodactylum tricornutum
PDF Search Title:
Red Light Variation Lipid Profiles in Phaeodactylum tricornutumOriginal File Name Searched:
applsci-10-02531.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Cruise Ship Reviews | Luxury Resort | Jet | Yacht | and Travel Tech More Info
Cruising Review Topics and Articles More Info
Software based on Filemaker for the travel industry More Info
The Burgenstock Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
Resort Reviews: World Class resorts... More Info
The Riffelalp Resort: Reviews on CruisingReview website... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@cruisingreview.com | RSS | AMP |